MRP glossary TOP > G > General Inventory Goods
General Inventory Goods
General Inventory Goods
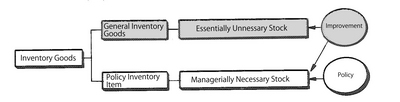
They refer to such items that their inventory is essentially accumulated in the process of manufacturing the product for the reasons below. This inventory is unavoidable for its manufacturing system and is unnecessary one from the management's point of view, for which General Inventory Goods are also called Passive Inventory Goods.
In contrast with General Inventory Goods, the items which are actively stocked from the management's point of view are called Policy Inventory Item.
Related term: Inventory Goods
They refer to such items that their inventory is essentially accumulated in the process of manufacturing the product for the reasons below. This inventory is unavoidable for its manufacturing system and is unnecessary one from the management's point of view, for which General Inventory Goods are also called Passive Inventory Goods.
- Inventory caused by the imbalance in capacity:
- When the capacity of pre-process is high and that of post-process is low, the inventory increases as naturally as water overflows.
- Inventory caused by less frequent arrangements:
- It takes quite much time to arrange, and thus the work in only large lots is needed, where even goods unnecessary at that point are created at a time, resulting in the creation of inventory.
- Inventory caused by neglected allocation:
- Both the case of the inaccurate grasp of inventory status and the case where the allocation for the goods are not made at planning due to they are originally nonstocked goods lead to the creation of inventory.
- Inventory caused by too much inventory on hand at the end of the month:
- This case often happens when directions are made to the site without reviewing the initial production plan by month. In the assembling process, a surge in production occurred in the last five days of the month, resulting in too much inventory of assembly parts in the factory for the period from the mid to the end of the month.
- Inventory caused by neglected review of the standards:
- No review is made after the standards of lead time, lot quantity, and Failure Rate were initially set, in most cases of which items are entered earlier than scheduled or extra goods are produced in preparation for the case many defectives are found, resulting in the creation of inventory.
In contrast with General Inventory Goods, the items which are actively stocked from the management's point of view are called Policy Inventory Item.

Related term: Inventory Goods
Reference:JIT Business Research Mr. Hirano Hiroyuki
