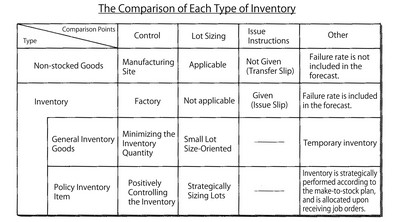
Inventory Goods
In production activity, a factory handles so many items. Thinking of those items from the standpoint of inventory, they are divided into two: the items to be sent via a warehouse and the ones to be sent from one process directly to another. The former is usually called Inventory Goods, while the latter is called Nonstocked Goods. Even if the goods are not actually stored in a warehouse and just put aside the process, they are handled as inventory goods as long as they are controlled to be provided to the plan. In addition, inventory goods are roughly divided into two types: they are proactively and strategically stored (not meaning "having much inventory"); they are stored without explicit purpose for the manufacturing division's reason. The former is called Policy Inventory Item, while the latter is called General Inventory Goods.
The Policy Inventory Item and General Inventory Goods mainly have the following features, respectively:
[Policy Inventory Item]
* inventory set to reduce the delivery lead time to customers
* inventory for speculative buying or policy buying
* inventory for service* inventory to standardize parts
* inventory to decrease the seasonal variation or production peak
[General Inventory Goods]
* inventory caused by the imbalance in capacity
* inventory caused by less frequent arrangements
* inventory caused by neglected allocation
* inventory caused by once-a-month production (too much inventory on hand at the end of the month)
* inventory caused by the use of obsolete standards (lot size, lead time)
The features are shown in the table:
Related term:
Item

