MRP glossary TOP > The functional roles an MRP production control system performs > Cost Control
Cost Control
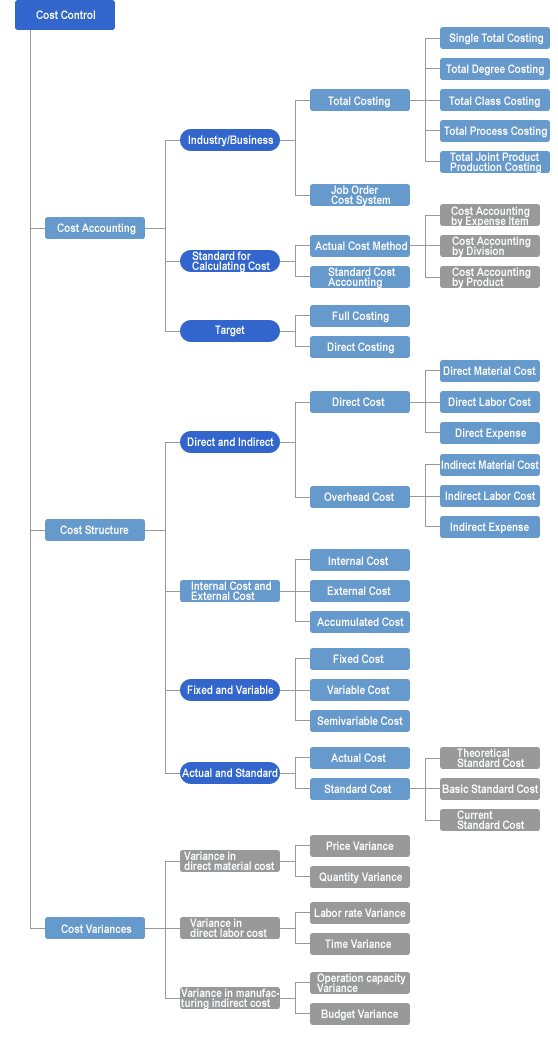
- Work descriptions:
-
It is a main operational function for manufacturing companies to produce products meeting given quality standards at the lowest cost until the scheduled delivery date. An enterprise is an organization that seeks a profit, for which the cost must be controlled.
The cost control is to replace the operational waste with a general scale of money (cost) common to the whole business activities, and to thoroughly eliminate waste. In other words, it is to consider "how to eliminate waste" from the point of view of money and make an improvement.
The cost calculation for cost control has three main objectives:
1) to identify the person in charge, and then measure and evaluate his/her performance;
2) to report the performance result to the manager of an enterprise;
3) to make an assessment on what level the improvements are made to, and what influence they had on the performance.
These control activities are usually handled by a division called the budget or accounts division. The budget division sets a standard cost, while the accounts division calculates the cost and prepares various reports. Specifically the works are as follows:
1) to set a cost category according to functional responsibility;
2) to set a standard cost;
3) to implement a costing system to compare to the actual performance;
4) to analyze the difference between the standard cost and the actual one;
5) to investigate and analyze the causes;
6) to report the result;
7) to take measures using the report.
These activities will lead all those involved in the organization to receive the motivation to increase the productivity, resulting in the implementation of cost-reduction activities and the elimination of waste. - Problems:
-
Possible problems in the cost control system are as follows:
1. The awareness of quality is low in whole.
2. Since cost calculation is performed for the purpose of financial accounting, the cost data is not precise.
3. The information is provided and grasped as a cost data too late.
4. The cost data is not effectively exploited for management decision making or management control.
5. The conventional cost calculation system can not follow up the transition to the high-mix low-volume production. - Functions:
- The system uses the B/M to consider the direct and indirect costs of all items including products, assemblies, parts, and raw materials, and then perform the standard costing by product. It also use the cost data submitted from the process control, receiving/inspection control, and other systems to prepare a cost table by expense item, division, product, which are necessary for the cost control.
Reference:JIT Business Research Mr. Hirano Hiroyuki
Quality Control | The functional roles an MRP production control system performs | Demand Forecast
