MRP glossary TOP > The functional roles an MRP production control system performs > Material Requirements Planning
Material Requirements Planning
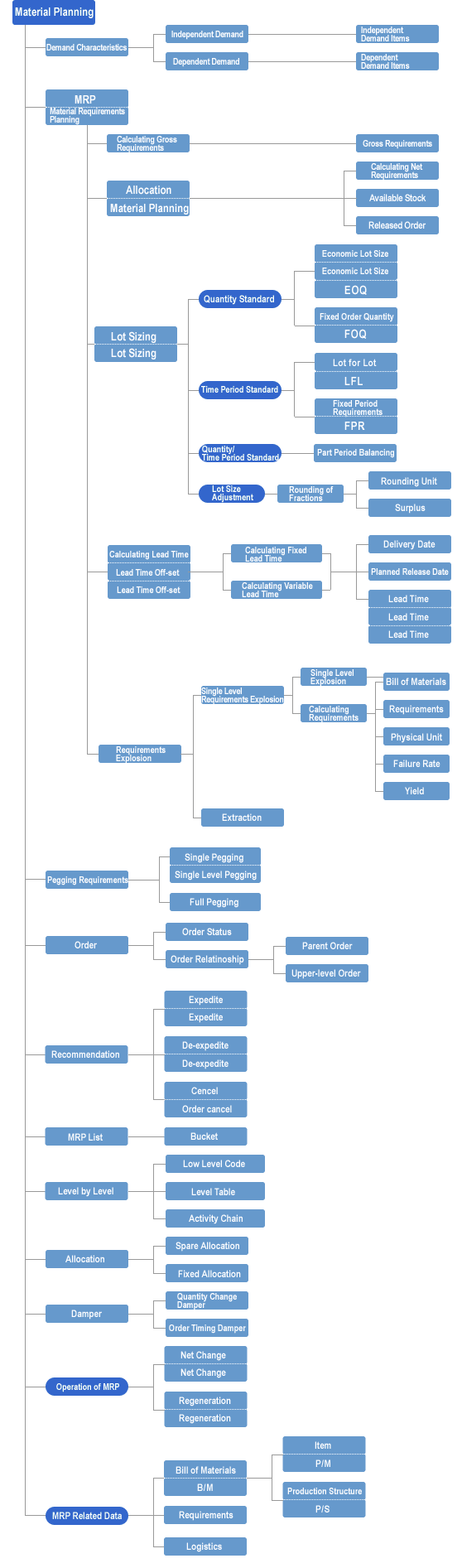
- Work Descriptions:
- It requires a number of items including assemblies, parts, and raw materials to produce a product, and each operation is individually performed by materials, purchasing, or manufacturing (processing and assembling) division, or each subcontractor.
- Problems:
- The problems of material planning are as follows:
1. The purchasing and manufacturing schedules are not controlled in a unified manner, making the change or rescheduling difficult to make.
2. In spite of much inventory, the loss in products often occurs and the persons in charge of procurement are too busy with the arrangement.
3. The appropriate lead time is not set and the explicit delivery date is not specified, which may lead to the loss in products and excesseive inventory.
4. It take too much time to place an order after receiving the production plan, making the actual manufacturing time shorter. - Funtions:
- How much/many (requirements) of what (item) is needed by when (delivery date) is calculated, and the logistics for purchasing and manufacturing them are performed. The data of assemblies, parts, and materials, which are planned by MRP, are sent to the purchasing division (in case of purchased parts and subcontact goods) of the manufacturing planning division (in case of manufactured item).
Reference:JIT Business Research Mr. Hirano Hiroyuki
Demand Forecast | The functional roles an MRP production control system performs
