MRP glossary TOP > The functional roles an MRP production control system performs > Purchasing Planning and Acceptance/Acceptance Inspection Control
Purchasing Planning and Acceptance/Acceptance Inspection Control
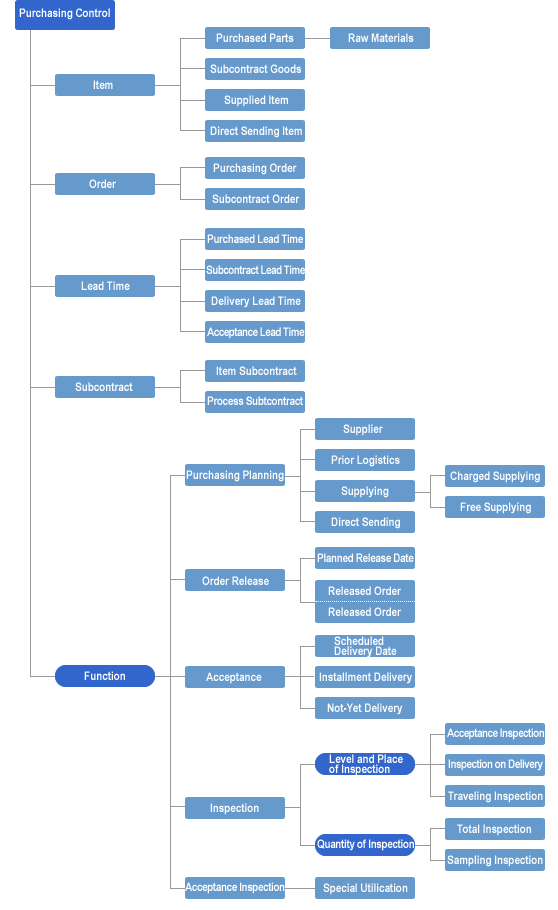
- Work descriptions:
-
Purchasing work is a trade activity. This is because whether or not one can buy at a high or low price depends on the way of one's buying. The quality of purchased materials also puts a direct influence on the final quality of the product, while the material cost accounts for the largest share of the total costs of the product. On top of that, meeting the delivery schedule of the purchased parts and subcontract goods ensures meeting the deadline of the product. Thus it is a purchasing work that directly influences QUALITY, COST, DELIVERY of the final products.
Considering that buying parts and materials is essentially based on the transactional relationship with other companies, and therefore it is important to fully grasp the status of subcontractors and to conduct proper and planned activities in order to make purchases smoothly. - Problems:
-
Possible problems in the purchasing control system are as follows:
1. Frequent changes in production plan are difficult to reflect in the purchasing plan.
2. Neglected or wrong logistics for necessary parts occurs too frequently.
3. Since timely placing orders and delivering is often based on the practical relationship with suppliers, it is hard to more carefully order and reduce the lead time.
4. Failing to understand the supplier's capacity and delivery performance makes it difficult to make planned orders.
5. Too many jobs of collecting and expediting makes the essential purchasing jobs difficult to perform.
6. Since the control of supplied items is insufficient, the place where they are put is not properly grasped and they may be lost or incomplete, which produces waste.
7. Ledger sheets and documents are manually prepared, which is a waste of time.
8. The subsequent observation of delivery date for each order made is insufficient, which causes the delivery to be frequently delayed.
9. The partial delivery or delayed settlement of the order unit price causes slow responses, which brings some troubles.
10. Since the result of inspection of goods delivered from all suppliers is not grasped, objective evaluations of suppliers are difficult to make. - Functions:
-
The purchasing control system has the functions of purchasing plan and receiving/inspection control.
Purchasing plan
Regarding the purchased parts or subcontract goods planned by MRP, the system reviews the number of order, selects suppliers, sets the order unit, specifies the date when the goods are delivered from the supplier, and fixes a scheduled inspection date. At this point, it checks whether or not the amount of the goods ordered to each supplier excesses its capacity, and, in case of subcontract goods, plans how to provide necessary supplied items to each supplier. Thus, after making purchasing plans, it makes these orders to suppliers on the scheduled day, which are formally controlled as unfulfilled purchase orders.
Receiving/inspection control
For the Purchasing Order or Subcontract Order made through the purchasing plan, the system makes the subsequent observation of delivery date, by which orders to be delivered in near future and the delivered orders can be checked. At the same time it makes a list of orders to be delivered, according to which it urges and expedites the delayed orders.
The delivered orders are also put in storage through the receiving, test, and inspection processes. Then, it records these statuses, grasps such data by supplier as the price variance, the number of rejected goods, and the number of delayed delivery, which are used for the next purchasing activities and evaluation/guidance for suppliers.
Reference:JIT Business Research Mr. Hirano Hiroyuki
Engineering Data Control | The functional roles an MRP production control system performs | Manufacturing Process Control
